Fastener Basics
Common Fastener Types
-
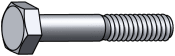
Hex bolts, or hex cap screws, are used in machinery and construction. Can be used with a nut, or in a tapped hole. Fully threaded hex bolts are also known as tap bolts
-
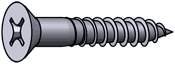
Wood screws have large threads and a smooth shank f or pulling two pieces of material together. They can be used in wood and other soft materials.
-
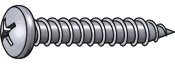
Sheet metal screws have sharp points and threads, and are designed to be driven directly into sheet metal. They can also be used in softer materials like plastic, fiberglass, or wood.
-
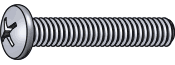
Machine screws are fully threaded for use with a nut or in a tapped hole. Certain types are some- times referred to as stove bolts.
-
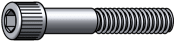
Socket screws are machine screws with an internal hex socket (Allen) drive. Longer lengths may have a smooth shank.
-
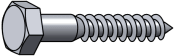
Lag bolts, or lag screws, are large wood screws with hex heads. Typically used for wood construction and landscaping.
-
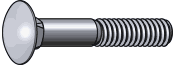
Carriage bolts have smooth, domed heads with a square section underneath that pulls into the material to prevent spinning during installation.
-
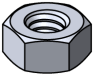
Nuts are used to fasten machine threaded fasteners in through-hole applications. Lock nuts help prevent loosening.
-
Washers spread the load over a greater surface area when tightening a bolt, screw or nut. Lock washers help preventing loosening.
Tip: See our full Fastener Type Chart for a more comprehensive list of fastener types.
Grade/Class & Fastener Strength
Fastener Grade (US) or Class (metric) refers to the mechanical proper- ties of the fastener material. Generally, a higher number indicates a stronger, more hardened (but also more brittle) fastener.
Tip: See Bolt Depot's Grade Markings and Strength Chart for a more comprehensive chart of fastener grades, head markings and mechanical properties.
US Bolt Head Markings
 Low carbon
Low carbon
 Grade 5
Grade 5
 Grade 8
Grade 8
Metric Bolt Head Markings
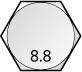 Class 8.8
Class 8.8
 Class 10.9
Class 10.9
 Class 12.9
Class 12.9
Fastener Materials
Note: Do not rely on this guide for color-matching. The appearance of these materials sometimes differs significantly from the photos below.

 Zinc-plated steel is a
low carbon steel for
general use. Relatively
inexpensive, with the
zinc plating providing
moderate corrosion
resistance suitable for
indoors or otherwise
dry conditions. Color is
either a blue-ish tint or
yellow depending on the exact process.
Zinc-plated steel is a
low carbon steel for
general use. Relatively
inexpensive, with the
zinc plating providing
moderate corrosion
resistance suitable for
indoors or otherwise
dry conditions. Color is
either a blue-ish tint or
yellow depending on the exact process.
 Hot-dipped galvanized
steel has a thicker zinc
coating for better
corrosion resistance,
making it suitable for
outdoor use. Because
of the thick plating,
only galvanized nuts and washers will fit
galvanized bolts. The coating typically has a
rough, dull grey finish.
Hot-dipped galvanized
steel has a thicker zinc
coating for better
corrosion resistance,
making it suitable for
outdoor use. Because
of the thick plating,
only galvanized nuts and washers will fit
galvanized bolts. The coating typically has a
rough, dull grey finish.
 Stainless steel offers
good corrosion
resistance, making it
suitable for outdoor
use and marine
applications, but is
more expensive than zinc plated.
Stainless steel offers
good corrosion
resistance, making it
suitable for outdoor
use and marine
applications, but is
more expensive than zinc plated.
 Chrome and nickel
plated steel are
smooth and polished
for appearance. The
plating offers moderate corrosion resistance.
Chrome and nickel
plated steel are
smooth and polished
for appearance. The
plating offers moderate corrosion resistance.

 Brass and bronze are
copper alloys with good
corrosion resistance.
More expensive than
steel, these materials
are typically used for
decorative applications.
Colors can vary
significantly.
Brass and bronze are
copper alloys with good
corrosion resistance.
More expensive than
steel, these materials
are typically used for
decorative applications.
Colors can vary
significantly.
 Alloy steel is highly
hardened and usually
black oxide and/or oil
coated, offering little
corrosion resistance.
Alloy steel is highly
hardened and usually
black oxide and/or oil
coated, offering little
corrosion resistance.
How Fasteners are Notated: An Example

type
type
style
count
(TPI)
Drive Types
-


Phillips and Slotted drives are common in screws, but prone to cam-out (stripping).
-

Combo drives, that can be used with either driver, are available for many fastener types
-


Frearson and Pozidriv are similar to Phillips, but less prone to cam-out.
-

Hex socket (Allen) drives are compact and easy to drive, but prone to cam-out.
-


Star (Torx™) and Square drive (Robertson) are resistant to cam-out and can be installed single- handed.
Note: Most drive types (Frearson and Slotted being notable exceptions) require the correct driver size for proper installation.
Head Styles
-
Hex heads are typically used with larger bolts and screws, and tightened with a wrench.
-

Pan heads have a slightly domed head that sits above the surface.
-
Flat heads are installed in a countersunk hole for a flat surface.
-
Round heads are tall domed heads, used primarily for decorative purposes.
-
Oval heads are a low domed and countersunk heads, used primarily for decorative purposes.
-

Truss heads are slightly domed, with a wide head for an extra large surface area.
-
Socket heads are narrow with a socket drive, and knurled or smooth sides.
-
Button heads feature a medium dome. Typically used with a hex socket drive.
Measuring Diameter

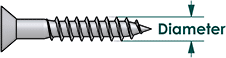
For most types of fasteners, the diameter is measured on the outside of the threads.
Note: US diameters under 1/4” are given as numbers (e.g. #12) instead of inches, in order of increasing size. If you need to find the actual diameter, use a table corresponding to your fastener type at https://boltdepot.com/info
Thread Count & Thread Pitch
Machine threaded fasteners specify a thread density in Threads Per Inch (US) or as a Thread Pitch in mm (Metric).
For a given diameter, a fastener may be available in coarse (standard), fine and sometimes super fine thread.
Measuring Length

Fastener length is usually measured from where the material is assumed to be to the end of the fastener.

Thus, countersunk fasteners are measured overall and non-counter- sunk fasteners are measured from under the head.
